|
|
AMV Product Display Information
AMV Level/Height Information:
AMVs are grouped into specified layers within each
product for display purposes. Layers are given in pressure units of
either millibars or hectopascals (which are equivalent).
| mb |
km |
feet |
| 150 |
13.7 |
45000 |
| 250 |
10.5 |
34000 |
| 350 |
8.0 |
26500 |
| 500 |
5.5 |
18000 |
| 600 |
4.3 |
14000 |
| 700 |
3.0 |
10000 |
| 850 |
1.5 |
5000 |
| 950 |
0.5 |
1500 |
|
The AMVs are assigned a level (mb) height. However, for display on
the CIMSS Tropical Cyclone Page, the winds are grouped into the layers
shown below to allow for easy identification of atmospheric feature
heights (e.g. hurricane outflow, jet streams, and upper level circulation centers).
Information on wind derivation and specific uses can be found at the links below.
Mid-Upper Level Water Vapor and Infrared Winds
150-250mb
251-350mb
351-600mb
Low-Mid Level Infrared Winds
400-599mb
600-799mb
800-999mb
Low Level Visible/Shortwave Infrared Winds
600-800mb
800-950mb
AMV Speed/Direction Information :
Wind vectors are labeled using "wind barbs". Direction is given by the orientation
of the post, with speed given by the barbs/flags at the end of the post. The head
of the post is the location at which the wind was determined. Speeds are indicated
using three symbols : a "flag" (triangle) indicating units of 50, a "full-barb" (long line)
indicating units of 10, and a "half-barb" (shorter line) indicating units of 5.
1 knot (nautical mile/hour) is approximately 1.15 miles/hour or 0.51 meters/second.
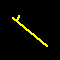 |
5 knot wind from the
northwest. One half-barb. |
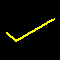 |
10 knot wind from the
southwest. One barb. |
 |
30 knot wind from the
northeast. Three barbs. |
 |
35 knot wind from the
southeast. Three barbs and one half-barb. |
 |
50 knot wind from the
northwest. One flag. |
 |
75 knot wind from the
south-southwest. One flag, two barbs, and one half-barb. |
 |
110 knot wind from the
southwest. Two flags and one barb. |
|
|
Analysis and Products:
AMV are extracted automatically every 3 hours from GOES, METEOSAT, and MTSAT data
producing near real-time wind fields and the related atmospheric analysis
products over all basins - NE/SE/NW Pacific, North Atlantic, East Atlantic and
Africa, Indian and W/E Australia.
Link to real-time products here.
The wind vectors can be used qualitatively by TC forecasters help visualize
the wind field around TCs, as well as quantitatively within numerical weather
prediction (NWP) models. Atmospheric analysis products, such as
deep layer wind shear,
mid layer wind shear,
wind shear tendency,
vorticity,
divergence, and
convergence
can be also be derived from these wind fields.
For more AMV information, please visit the
International Winds Working Group (IWWG)
page.
|
|
|